In the last post I showed you some of the products I created at the very beginning of my career as a product creator. In this post I want to show you my product creation life span.
I followed a pattern and it worked but what I wasn’t told, is how fragile these products are. So dependant on other factors.
So after a couple of years lots of people saw how successful I was and so started to go in competition with me.
So there was a flurry of streaming audio products that came on the market which meant my sales started to slow. The next thing was technology started to change and I was able to upgrade for some of it.
You can see some of my efforts for these products on my youtube channel. Look to the beginning.
So lets break it down for you.
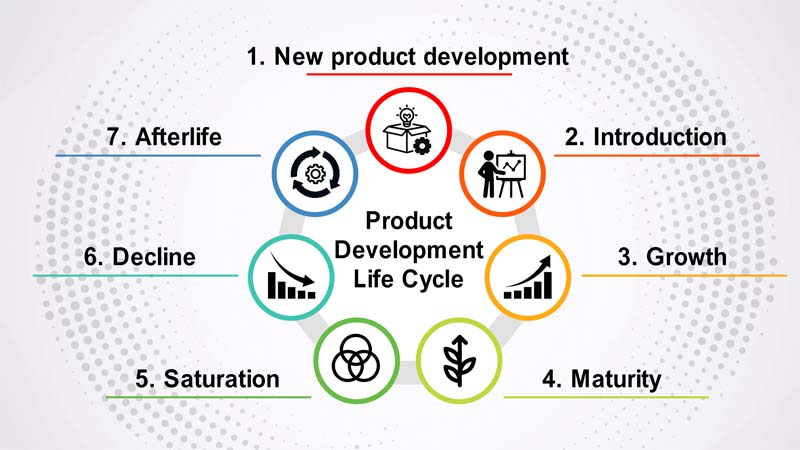
The Product Creation Lifespan
The product creation life span refers to the process of developing a new product, from its conceptualization and design to its launch and eventual retirement from the market.
This product creation life span can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the product, the industry, and the market conditions.
Let me lay it out for you and we will explore the key stages of the product creation life span, the challenges faced during each phase, and the strategies that can contribute to a successful product development journey.
Stages of Product Creation Life Span:
- Idea Generation: The product creation process begins with the generation of ideas. This stage involves brainstorming, market research, and identifying gaps or opportunities in the market. The goal is to come up with innovative and viable product concepts.
. - Concept Development: In this stage, the most promising ideas are further refined and developed into product concepts. Key features, specifications, and target market segments are defined. At this point, a feasibility study may be conducted to assess the product’s viability.
. - Design and Prototyping: Once the concept is finalized, the design phase begins. Product designers and engineers create detailed plans and prototypes to visualize and test the product’s functionality, appearance, and usability.
. - Testing and Validation: During this stage, prototypes are subjected to rigorous testing to ensure that they meet quality standards and perform as expected. User feedback is collected, and necessary improvements are made.
. - Manufacturing and Production: With a validated prototype, the product moves to the manufacturing phase. This involves setting up production processes, sourcing raw materials, and ensuring quality control measures are in place.
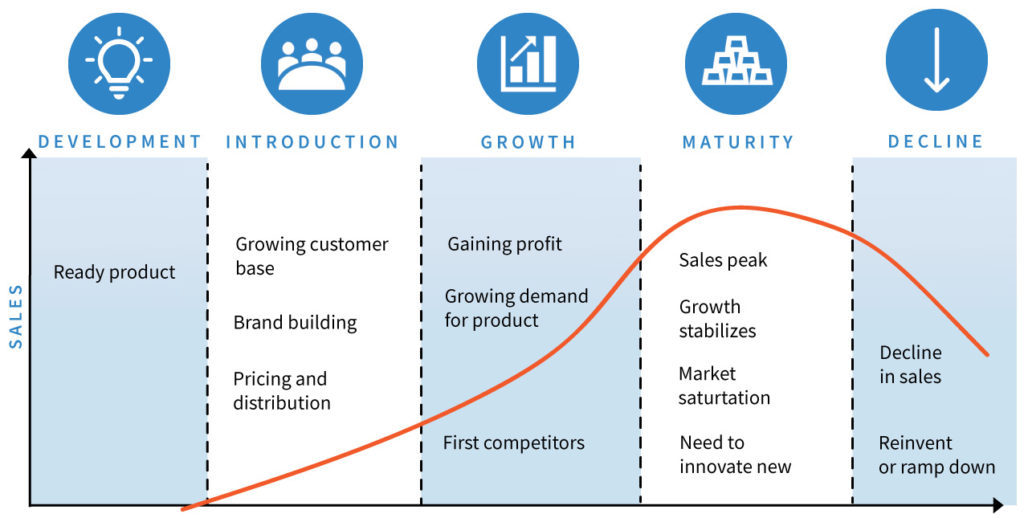
. - Launch and Market Introduction: The product is officially launched and introduced to the market. Marketing and promotional efforts are critical during this phase to create awareness and drive initial sales.
. - Growth and Market Penetration: Assuming the product is well-received, it enters a phase of growth and market penetration. Sales and distribution channels are expanded to reach a wider customer base.
. - Maturity and Sustenance: The product reaches its peak maturity, and sales stabilize. Companies focus on maintaining market share, customer loyalty, and continuous improvement to extend the product’s life span.
. - Saturation and Decline: As the market becomes saturated or newer products emerge, sales growth may slow down, leading to a decline in the product’s life span.
. - End of Product Creation Life Span and Retirement: Eventually, the product becomes obsolete or unprofitable to maintain, leading to its retirement or discontinuation from the market.
Challenges and Strategies:
- Market Research: Inadequate market research can lead to the development of products that do not meet customer needs or have limited demand. Conducting thorough market research and understanding customer preferences is crucial.
. - Product Development Delays: Lengthy product development cycles can result in missed market opportunities. Streamlining the development process and efficient project management are essential.
. - Cost Management: Balancing product development costs with profitability is a challenge. Companies should carefully manage expenses throughout the life span of the product.
. - Competition: The presence of competitors can impact a product’s success. Creating a unique value proposition and staying ahead of the competition is vital.
. - Regulatory Compliance: Products must meet regulatory standards and requirements, which can be challenging in highly regulated industries.
. - User Feedback: Ignoring user feedback and failing to address customer concerns can lead to product failure. Companies should actively seek and respond to user feedback.
. - Adaptability and Flexibility: Market conditions may change, and products may need to be adapted or updated to remain relevant. Flexibility in responding to market trends is crucial.
. - Marketing and Promotion: Effective marketing and promotion are necessary to create awareness and drive sales during the launch and growth stages.
The product creation life span involves multiple stages, each with its unique challenges and opportunities.
While these are the documented stratigies I have learnt over time the reality is that much of it was just done without realising what they were.
The real keys for me were psaaion about the product, customer feedback and research. Also I was giving to charity which took a lot of the spotlight off me and the money. Its important to have an outside interest for you product creation life span endeavours.
It gets to the point where you have to move on or relaunch a whole new product.
I decided that I had made a fair bit so I decided to go and follow a dream of working in the charity sector again and so moved to Thailand with my wife and younger son to train some of those orphans we were sponsoring way back when I moved to Brisbane.
I loved teaching them web design and Photoshop plus lots of other skills and most of them got hired by companies and NGO’s or started their own businesses and some have done very well.
As I started to teach these young people I created a website and tutorials for them to update their skills and also for revision. So in reality that is what I based this site on as I offer it for free to some of their friends etc,
So I moved from software developer to training and education.
It wasn’t long after and apple released the first iPhone and life changed again.
See you in the next episode.